What are bacterial and viral infections?
Bacteria and viruses can cause mild to severe infections. It is crucial to differentiate bacterial and viral infections because both types of infections require distinct treatments.
There are some similarities between viruses and bacteria, including:
- They are too minute to be seen by the naked human eyes.
- They often spread or being transmitted in the same manner such as through coughing, sneezing, and physical contact with infected individuals.
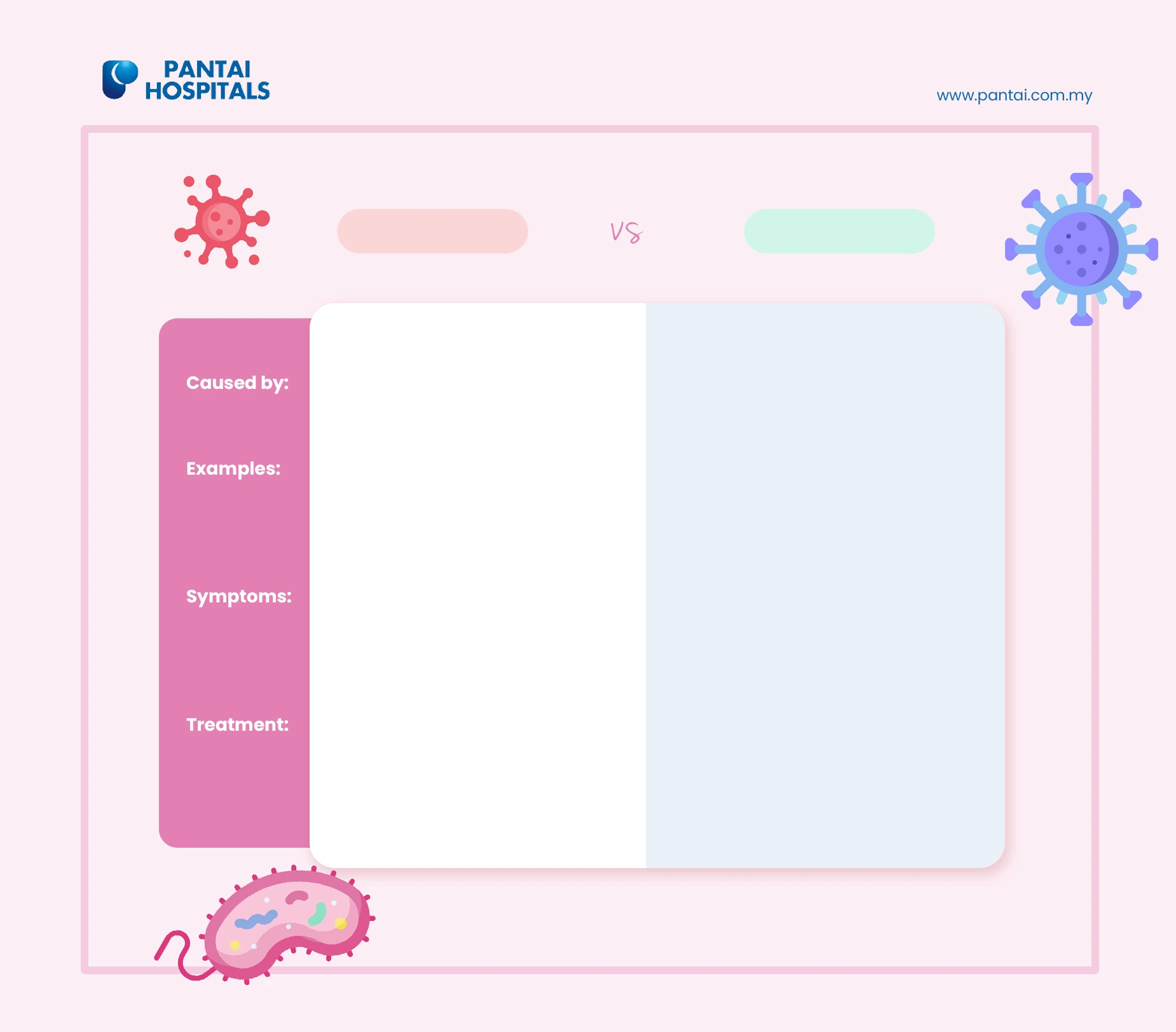
Examples of diseases caused by bacterial infection:
- Tuberculosis
- Urinary tract infections
Examples of diseases caused by viral infection:
- Influenza
- COVID-19
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Rotavirus
- Hepatitis A, B
- Chicken pox
Certain diseases such as pneumonia and meningitis could be caused by either bacteria or virus.
Symptoms of viral and bacterial infections are similar such as fever, flu, coughing, diarrhoea, vomiting, body ache, sore throat, lethargy.
Do take note that the infections can only be differentiated by conducting blood or urine tests to confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes, culture tests are conducted to identify the type of bacteria or virus that causes the infection.
What are the treatments available for bacterial and viral infections?
Treatments for bacterial infection
Bacterial infection is commonly treated with antibiotics as they either destroy the bacteria or prevent the growth of bacteria.
However, as antibiotic resistance is on the rise, antibiotics should only be used to treat severe bacterial infections.
Treatments for viral infection
There are no specific treatments for viral infections. Typically, viral infections are managed by treating their symptoms. This frequently entails the use of over-the-counter pain medicines to relieve symptoms such as pain, fever, and lethargy.
Antivirals are medicines used to combat viral infections. Antivirals are only used for certain viral infections such as hepatitis, influenza. and herpes.
Vaccines provide protection against particular viruses by conditioning the immune system to recognise and attack a specific virus.
Caution!
Remember: Antibiotics are not effective in treating viral infections. Antibiotic resistance is exacerbated by the improper use of antibiotics to treat viral infections.
Bacteria
Infection
Bacteria
Infection
Viral Infection
Viral Chemotherapy
Make an appointment at Pantai Hospitals
In some instances, it is quite challenging to differentiate both types of infections due to similar symptoms, such as the common cold.
A common cold may not be life-threatening to most people. However, if you are experiencing other symptoms that you are unfamiliar with, it is best to make an appointment and consult your doctor for prompt medical attention.
References
- Ansorge, R., Bacteria and Viral Infections, WebMD, 17 Apr 2021. Available at https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/bacterial-and-viral-infections [Accessed 15 Aug 2022]
- CDC, Antibiotics Aren’t Always the Answer, CDC, 8 Nov 2021. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/patientsafety/features/be-antibiotics-aware-infographic.html [Accessed 15 Aug 2022]
- ESWI, Difference between Vaccines, Antivirals and Antibiotics, ESWI. Available at https://eswi.org/knowledge-center/difference-between-vaccines-antivirals-and-antibiotics/ [Accessed 15 Aug 2022]
















