
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder. It is typically diagnosed when one has consistent seizures, where the neurons or brain cells uncontrollably send out electrical signals, and cause disruption of normal communications between brain cells.
Seizures
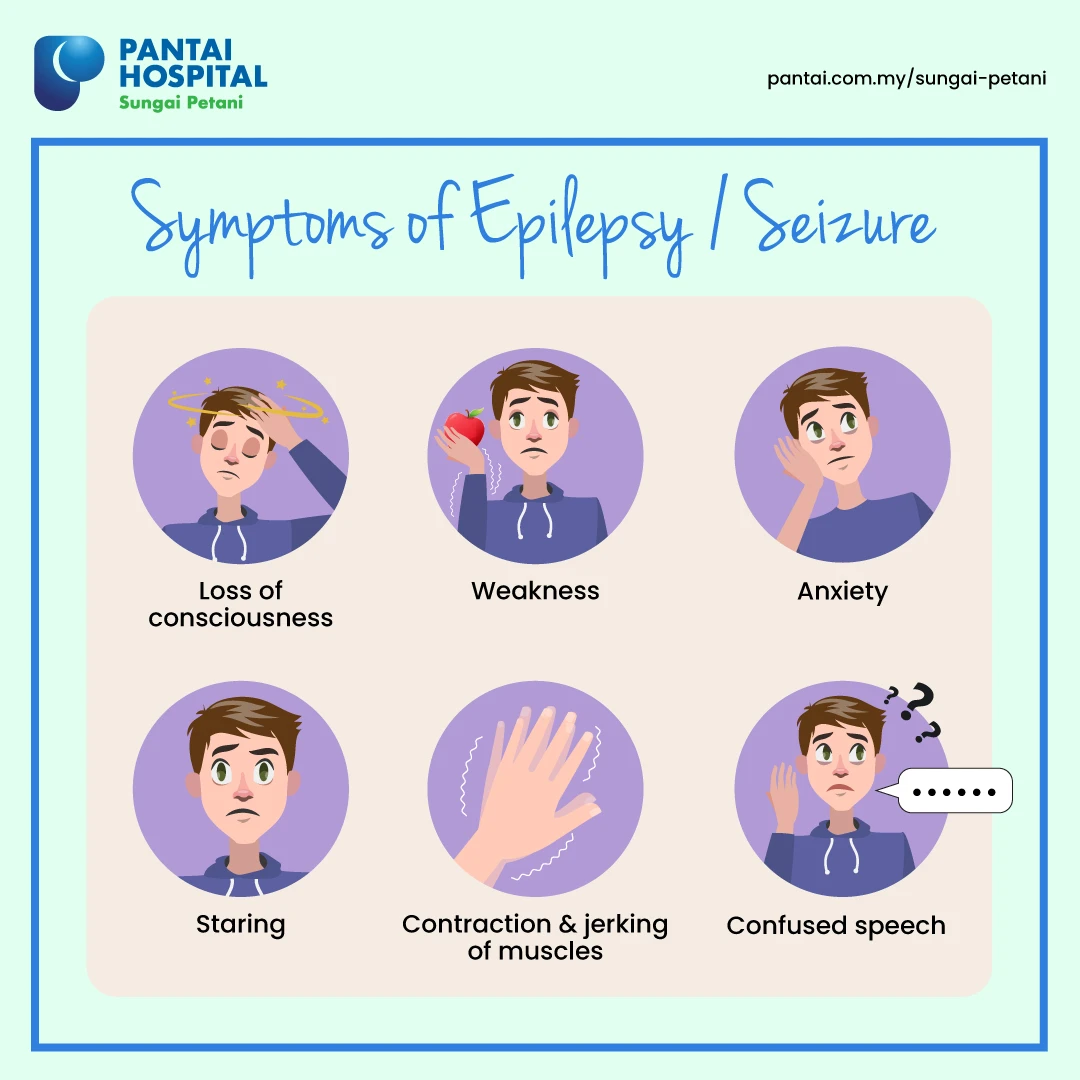
Seizures are sudden when many brain cells send signals at the same time. Imagine a traffic light system is overloaded by signals from multiple stations. The excessive electrical activity in the brain may cause involuntary movements and/or behaviours such as fall, shake, rapid blinking, seeming disconnected by staring at one spot and loss of consciousness. Most seizures last from few seconds to less than 5 minutes. You may need to call an ambulance if it lasts longer than 5 minutes.
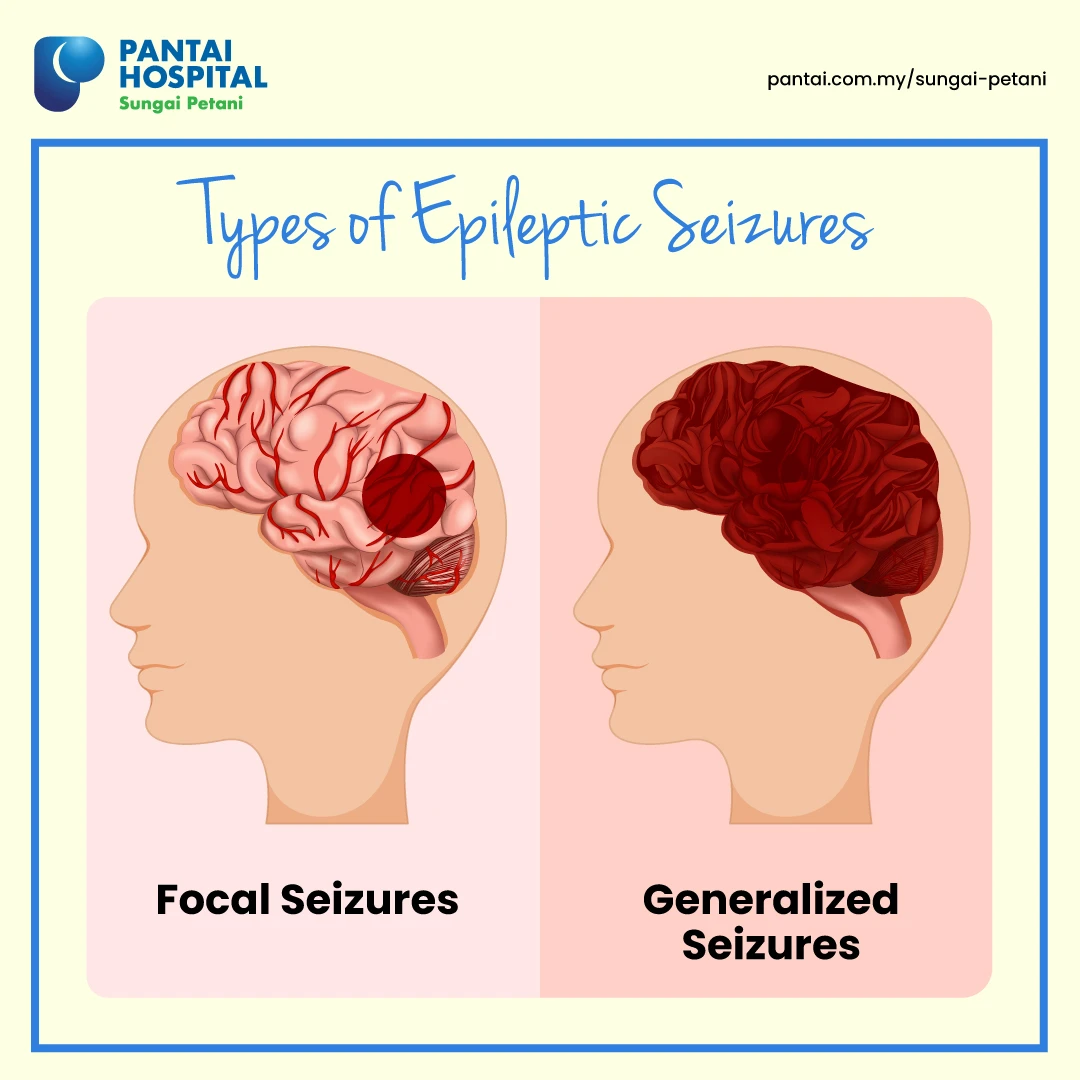
Seizure is mainly categorised into two groups based on its onset location: focal seizure and generalised seizure. Focal seizure happens at one specific area, while generalized seizure involves the entire brain.
There are many types of seizures. One may have single or recurring episodes of seizures, or more than one type of seizures. Having a single seizure doesn't help a neurologist to diagnose an epilepsy.
Causes
Diagnosis
The information is brought to you by Resident Neurologist, Dr Jayaganth Jayabal from Pantai Hospital Sungai Petani. To schedule an appointment with him, please click here.

