
Early detection result in early treatment
Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the lower front of the neck. It plays a role in the secretion of thyroid hormones, which are secreted into the blood and carried to every tissue in the body. Thyroid hormone is a hormone that controls the body's metabolism, affecting heart rate, temperature regulation, the digestive system, brain development and muscle contraction. The two main hormones released by the thyroid gland are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Hyperthyroidism refers to any condition in which there is excess thyroid hormone produced in the body. If there is too much thyroid hormone, every function of the body tends to speed up include : Nervousness, Irritability, Increased sweating, Heart racing, Hand tremors, Anxiety, Hair loss, Muscle weakness especially upper arms and thighs, Frequent bowel movements, Unintentional weight loss and Menstrual abnormalities.
The commonest cause of hyperthyroidism is overproduction of thyroid hormone by the entire thyroid gland, known as Graves’ disease. This condition is caused by antibodies in the blood that turn on the thyroid and cause it to secrete too much thyroid hormone. This type of hyperthyroidism can be familial and occurs more often in young women.
Another cause of hyperthyroidism is due to one or more nodules or lumps in the thyroid that may gradually grow and increase their activity, causing excess thyroid hormone secretion. These lumps may or may not be visible.
Some may temporarily have symptoms of hyperthyroidism in a condition called thyroiditis. This condition may be caused by viral or other infections or problems with the immune system causing the gland to leak stored thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism is treated with medications, radio-iodine therapy or by surgery.
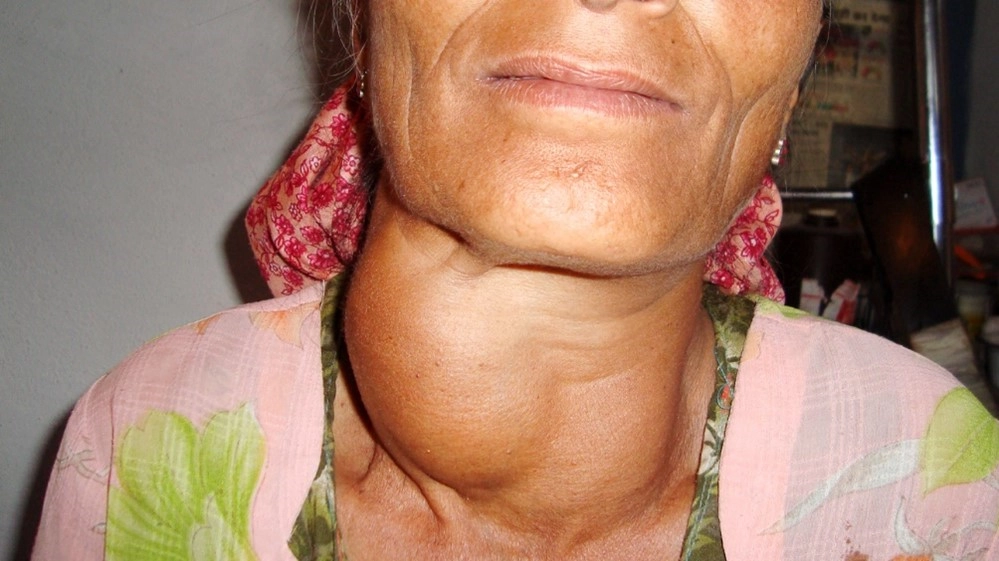
Hypothyroidism is a condition of thyroid underactivity where the thyroid gland is unable to make enough thyroid hormone to keep the body functioning normally. Common causes are due to the immune system attacking the thyroid gland and damaging it - a disease called “Hashimoto’s thyroiditis”, as a side effect or complication of previous treatment to the thyroid gland, such as surgery or a treatment called radioactive iodine therapy.
When thyroid hormone levels are too low, the body’s cells can’t get enough thyroid hormone and the body’s processes start to slow down. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include: tiredness, being sensitive to cold, weight gain, constipation, depression, slow movements and thoughts, muscle aches, cramps and weakness, dry and scaly skin, brittle hair and nails and irregular periods or heavy periods.
Elderly people with hypothyroidism may develop memory problems and depression. Hypothyroidism is treated with thyroxine (t4) hormone replacement. Hypothyroidism may become more or less severe, and your dose of thyroxine may need to change over time .If you take your pills every day and work with your doctor to get and keep your thyroxine dose right, you should be able to keep your hypothyroidism well controlled throughout your life.
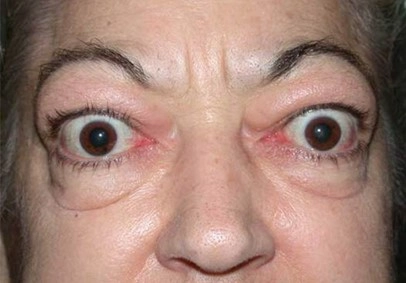
Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism can lead to heart problems such as irregular heart rhythm increasing the risk of stroke and heart failure. Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to weak, brittle bones , a condition called osteoporosis, thyroid eye disease and skin problems . Severe hyperthyroidism is a medical emergency and is life threatening
Untreated hypothyroidism may lead to enlargement of the thyroid gland causing swallowing or breathing difficulties, heart problems, increases in LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) and infertility. Infants with hypothyroidism may suffer from physical and mental developmental problems. . Severe hypothyroidism can cause a life-threatening condition.
A blood test measuring your hormone levels is the only accurate way to find out whether there's a problem. The test, called a thyroid function test, looks at levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) in the blood. Additional tests such as T3 levels, antibody tests and thyroid imaging may be also ordered by your doctor. Get tested if you suspect you have a thyroid problem and speak to your doctor to ensure your thyroid function is optimal.

This article was contributed by Dr. Tivya A/P Soundarajan, Endocrinologist and Physician of Pantai Hospital Ipoh. To know more about where and when to see Dr. Tivya at his clinic, click here.

